Understanding the difference between a business model and a business plan is crucial for entrepreneurs and business managers. While these two terms are often used interchangeably, they refer to distinct aspects of a business’s strategy and operations.
Get started with our forecasting software so that you can plan your business' futureTransform your business strategy with Brixx
What is a business model
A business model is a conceptual framework that outlines how a company creates, delivers, and captures value. It’s a strategic plan for earning profits, detailing the products or services the business will sell, the target market it aims to reach, and the expected costs and revenue streams. Essentially, it’s a blueprint that defines the way a company operates and makes money.
Examples of business models
- Subscription model:
This model is prevalent in companies like Netflix or Spotify. Customers pay a recurring fee, usually monthly or annually, to continuously access a service. This model provides steady, predictable revenue for the business and convenience for the customer. - Freemium model:
Popularized by companies such as Dropbox, this model offers basic services for free while charging for advanced or premium features. It’s a way to attract a large user base quickly, with the hope of converting a portion of those users into paying customers. - E-commerce model:
Companies like Amazon and Alibaba operate under this model, selling products directly to consumers or other businesses through online platforms. This model has revolutionized retail by offering a wide range of products with the convenience of online shopping and home delivery. - Advertising model:
Platforms like Facebook and Google use this model, where the primary revenue stream comes from advertising. These companies offer free services to users and sell targeted advertising space to businesses, leveraging the vast amount of user data they collect. - Direct sales model:
This traditional model involves selling products directly to consumers, bypassing intermediaries. Companies like Avon and Tupperware use this model, often combining it with network marketing strategies. - Franchise model:
In this model, a business (the franchisor) allows individuals (franchisees) to trade under the business’s name and sell its products or services. The franchisee will then pay an initial fee, alongside ongoing royalties to the franchisor. Examples include fast-food chains like McDonald’s and Subway. - Gig economy model:
Platforms like Uber and Airbnb exemplify this model. They provide a marketplace where individuals offer services (like ridesharing or lodging) to others. The platform facilitates these transactions and earns a commission from each booking.
Each of these models has its unique characteristics and strategies for creating value and generating revenue. The choice of a business model depends on various factors including the industry, target market, and the nature of the product or service offered.
While a business model is a conceptual framework outlining how a company creates value, a business plan is a more detailed and practical document that sets out specific business goals and the strategies to achieve them. The business model is the core concept around which a business plan is developed.
To further distinguish between a business model and a business plan, let’s consider them from various perspectives:
Metaphorical comparison
- Business model: Think of the business model as the blueprint of a house. It’s an overarching design that outlines the structure and functionality of the house – the type of house, its layout, the flow between rooms, etc.
- Business plan: The business plan is like the construction plan for building the house. It includes detailed specifications, materials, timelines, and the steps needed to build the house as per the blueprint.
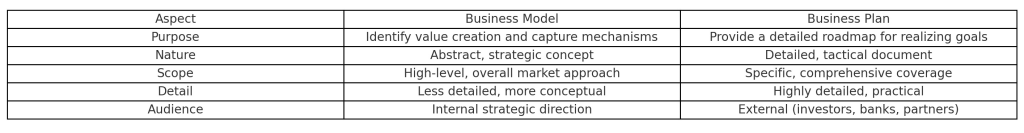
Purpose
- Business model: Its primary purpose is to identify how the business will create and deliver value to customers, and how it will extract economic value for itself. It’s about the company’s strategy for operating in the market.
- Business plan: The purpose of a business plan is to provide a detailed roadmap for realizing the business model. It’s used for operational planning, securing financing, and guiding the company’s growth and development.
Scope and detail
- Business model: Generally, business models are more abstract and high-level. They provide an overall picture of how the business intends to function in the market.
- Business plan: Business plans are detailed and comprehensive. They delve into specifics like market research, financial projections, marketing strategies, and operational details.
Audience
- Business model: Primarily designed for internal understanding and strategic direction of the company.
- Business plan: Often created with external audiences in mind, such as investors, banks, or potential partners, to convey the company’s strategy and operational plans.
Functionality
- Business model: It’s a conceptual tool used to explore and articulate the business strategy and innovative approaches to the market.
- Business plan: Serves as a practical tool for execution, guiding the day-to-day operations and long-term objectives of the business.
By considering these different aspects, it becomes clear that while a business model and a business plan are closely related, they serve distinct functions and have different focuses within the business structure and strategy.
This table outlines the main differences between a business model and a business plan across various criteria:
Transform your business strategy with Brixx
The business model serves as the conceptual blueprint for creating and capturing value, while the business plan provides a detailed roadmap for implementation.
Brixx emerges as an essential financial forecasting tool in this process. It offers a suite of features that effectively bridges the gap between the strategic planning of your business model and the practical execution of your business plan. Key features include dynamic financial modeling, strategic planning and forecasting, comprehensive cash flow management, scenario analysis, collaborative planning capabilities, and in-depth reporting and analysis.
For entrepreneurs and business managers looking to seamlessly integrate their business model with an actionable business plan, Brixx offers the perfect solution. Discover how Brixx’s business planning software can transform your business strategy into a tangible success story. Try Brixx today and take the first step towards a more streamlined and efficient business planning process.
- Recommended Reading: Financial Model vs Financial Plan
FAQs
Is a business model more important than a business plan, or vice versa?
Both are equally important but serve different purposes. The business model provides the strategic foundation, while the business plan outlines the tactical execution of that strategy.
Can a business operate without a formal business plan?
Yes, particularly in the early stages or in very small operations. However, as a business grows, a formal business plan becomes crucial for guiding strategy, securing financing, and managing operations effectively.
Should startups focus more on their business model or business plan?
Startups should first develop a solid business model to understand their value proposition and market fit. Once this is established, a detailed business plan is essential for guiding growth and securing funding.