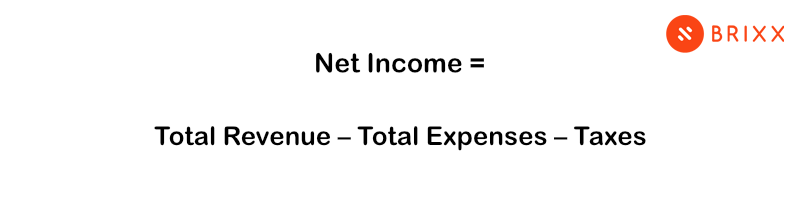Managing your business’ finances requires a firm grasp of financial concepts. One of these to be aware of is ‘net income.’
Whether you’re an individual striving to create a robust financial plan or a business owner aiming to assess your company’s profitability, understanding how to calculate net income is essential.
Get started with our forecasting software so that you can plan your business' futureAnalyze your income in Brixx
What is net income?
Net income, also known as profit or net profit, is a financial metric that represents the amount of money remaining to a business after deducting all expenses and taxes from their total revenue. In essence, it is the actual profit that remains once all the costs associated with generating revenue have been accounted for.
In the context of a business, net income is a measure of profitability. It is calculated by subtracting all operating expenses and other costs from the company’s total revenue. A positive net income indicates that the business is profitable, while a negative net income implies a financial loss.
Understanding and calculating net income is crucial to manage finances effectively and for businesses to evaluate their financial health and make informed decisions for the future.
Why is net income important for a business?
Net income is of paramount importance for a business for several compelling reasons. We have listed the top five below:
Assessment of profitability
Net income shows exactly how profitable a business has been. It indicates whether the company is making money or incurring losses. Positive net income shows a profit, while negative net income signals financial difficulties.
Cash flow management
Positive net income contributes to healthy cash flow, ensuring that a business has the resources to meet its day-to-day requirements, such as paying employees, suppliers, and bills.
Making important financial decisions
Businesses use net income to make critical financial decisions. It helps in determining how much money can be reinvested in the company. A strong net income can lead to better financing terms and increased borrowing capacity.
Instilling investor confidence
Investors will closely monitor a company’s net income as it influences their confidence in the business’s ability to generate returns. Consistently positive net income can attract investors and contribute to the growth of the business.
Benchmarking for evaluation
Net income allows businesses to compare their financial performance over time and against industry becnhmarks. It provides a standard measure to evaluate the effectiveness of cost control, revenue generation, and overall business operations.
To summarize, net income is a critical financial metric that not only reflects a business’s profitability but also influences a wide range of financial and strategic decisions.
How to calculate net income for your business
Calculating net income for your business involves subtracting all expenses from your total revenue. Here’s an easy guide on how to calculate net income:
Step 1: Gather your financial information
To calculate net income accurately, you’ll need your business’s financial statements. The key statements you’ll need are the income statement and the statement of cash flows.
Step 2: Determine your total business revenue
Identify your total revenue, which includes all the money your business generates from its primary operations.
Step 3: List any expenses
Create a comprehensive list of all operating expenses incurred during the accounting period.
Step 4: Include and interest
If your business has any outstanding loans or debts on which you pay interest, include the interest expenses in your calculation. This is typically found in the financial statements or loan agreements.
Step 5: Consider any taxes
Deduct income taxes from your total revenue. This amount will vary based on your business structure and tax regulations in your jurisdiction.
Step 6: Calculate Net Income
Subtract the total operating expenses, interest expenses, and income taxes from your total revenue:
Net Income = Total Revenue – Operating Expenses – Interest Expenses – Income Taxes
Step 7: Review and Interpret
Once you’ve completed the calculation, you’ll arrive at your business’s net income. A positive net income indicates profitability, while a negative net income suggests a financial loss.
Step 8: Analyze and make informed decisions
After calculating your net income, use this information to assess your business’s financial health and make informed decisions. You can compare your net income to previous periods, industry benchmarks, and your financial goals to evaluate your performance and plan for the future.
It’s important to note that net income is a key indicator of profitability, but it may not represent the actual cash flow available to the business. Cash flow can differ from net income due to factors like depreciation and changes in working capital. Therefore, it’s also essential to consider your cash flow statement in your financial analysis.
Net income formula
The net income formula is straightforward and consists of subtracting total expenses and taxes from total revenue. Here’s the net income formula:
Net Income = Total Revenue – Total Expenses – Taxes
- Total revenue: This represents all the money generated from various sources.
- Total expenses: This includes all costs and expenses associated with running the business.
- Taxes: This refers to income taxes paid to the government, which may include federal, state, and local taxes.
By using this formula, you can calculate the net income of a business, which represents the actual profit remaining after all expenses and taxes have been deducted from the total revenue.
Are there any net income limitations?
There are limitations and considerations associated with net income as a financial metric. It’s important to be aware of these limitations when using net income for financial analysis and decision-making. We have listed five limitations below:
Accrual Basis Accounting: Net income is calculated using the accrual basis of accounting, which means that it records revenue when it’s earned, and expenses when they’re incurred, not necessarily when cash changes hands. This can lead to discrepancies between net income and actual cash flow.
Non-cash expenses: Net income will contain expenses that aren’t cash, such as depreciation and amortization. While these expenses reduce net income, they don’t represent actual cash outflows.
Lack of real-time information: Net income is typically reported on a time-period basis such as quarterly or annually. It may not provide real-time insights into a company’s financial health, making it less useful for short-term decision-making.
Income tax variability: The amount of income tax a business pays can be influenced by various factors, including tax credits and deductions. This can lead to variability in net income from one period to another.
Inflation and currency fluctuations: Changes in inflation and currency exchange rates can affect the real value of net income, especially for businesses operating internationally.
Despite these limitations, net income remains a critical financial metric that provides valuable insights into a company’s profitability and financial health. To overcome some of the limitations, it’s advisable to use net income in conjunction with other financial metrics, such as cash flow, EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization), and various financial ratios, for a more comprehensive analysis.
How to use net income in financial decision making
Here’s how you can use net income in your financial decision-making process:
- A healthy net income can lead to more favorable financing terms and greater flexibility in funding opportunities, leading to better investment decisions
- Net income is essential for creating budgets and financial forecasts
- A strong net income can result in more favorable lending terms for loans
- Businesses use net income figures to calculate income tax liabilities and optimize tax strategies
- Comparing net income to industry peers and benchmarks helps businesses assess their profitability and competitiveness in the market.
By understanding your net income and using it as a starting point for financial planning, you can better manage your finances, make sound investment choices, and ensure the long-term financial health of yourself or your business.
Using Brixx to calculate net income
Using a financial forecasting tool like Brixx can be incredibly helpful in calculating net income for businesses. Such software helps streamline the process, manage financial data, and perform complex calculations.
Financial forecasting software simplifies the process of calculating net income and helps businesses create more accurate and informed financial projections, which is essential for effective financial management and decision-making.
Net income FAQs
Gross income vs net income
The key difference between gross income and net income lies in the scope of their calculations and the deductions they incorporate.
Gross income represents the total business revenue before any expenses or deductions are accounted for.
Net income is the amount left after all expenses have been subtracted from the total revenue. Net income reflects the actual profitability or disposable income, making it a more accurate indicator of financial health for both individuals and businesses.